Search
- 04/10/2023
Integrating Embedded WiFi Modules for Seamless Connectivity
In today's world, where the internet is the backbone of all technological advancements, seamless connectivity has become a necessity. Integrating WiFi modules into devices is one of the most significant challenges in achieving seamless connectivity. Embedded WiFi modules are becoming increasingly popular as they offer a cost-effective solution to integrating WiFi into a device.
Multiple types of embedded WiFi modules will be introduced to you in this article, such as Bluetooth WiFi modules and combo modules, and highlight the benefits and common application scenarios of each, discussing the benefits, challenges, and practices of integrating embedded WiFi modules for seamless connectivity.
What is an “Embedded” WiFi Modules?
Embedded WiFi modules are small devices that can be embedded in the systems of various applications to provide wireless connectivity to the network. In short, with the integration of an embedded WiFi module, the devices around you or in your hand can connect to the network quickly and smoothly. It typically comes with a small form factor, low power consumption, and a range of wireless protocols to suit different applications. They are commonly used in IoT devices, smart home appliances, healthcare, and industrial automation.
Types & Applications of Embedded WiFi Modules
- Single-Band WiFi Modules - These modules operate on the 2.4GHz frequency band and are the most common type of WiFi module. Most IoT devices have integrated these types of module to realize internet connection, including smart home devices, wearables, and industrial automation systems.
- Dual-Band and Triple-Band WiFi Modules - These modules can operate on both frequency bands, which are known as 2.4GHz and 5GHz, and the frequency can even be extended to 6~7GHz, providing improved performance and faster data transfer speeds compared to single-band modules. Dual-band /Triple-band modules are used in high-performance applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and high-speed data transfer.
- Combo WiFi modules - Also known as wireless combo modules, they feature WiFi and various wireless connectivity technologies in one module. Combo WiFi modules are trendy in the IoT market, offering a cost-effective solution for high-performance connected devices. The following are some of the most common types of combinations available on the market:
- WiFi Module with Bluetooth - WiFi is used for high-speed data transfer over shorter distances, while Bluetooth is used for low-power and low-bandwidth communication. This combination is commonly used in smartphones, laptops, and other mobile devices, enabling them to connect to wearable devices such as headphones or smartwatches.
- WiFi Module with LoRa - It enables long-range communication for IoT devices. LoRa technology uses low-power, long-range communication to provide connectivity over several kilometers, making it ideal for applications such as smart cities, agriculture, and industrial automation. This type of module is commonly used in remote monitoring and control systems, telemedicine (patient monitors), smart agriculture, and asset tracking in V2X.
- WiFi Module with GNSS - It combines WiFi technology with Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology to determine a device's location, speed, and direction. The WiFi capability suits it for data-intensive applications such as streaming or downloading maps. It is ideal for navigation systems, tracking devices, and geolocation services and provides accurate location information.
Challenges of Embedded WiFi Modules
1. Limited Range
One of the most significant challenges of embedded WiFi modules is their limited range. WiFi signals can be affected by various factors such as walls, obstacles, and distance. Devices that use embedded WiFi modules should be designed to operate within a limited range to ensure connectivity.
2. Interference
Interference from other wireless devices is also a common occurrence, especially when two devices operate on the same frequency at the same time. The interference can cause data loss, increased latency, and reduced network performance. To be able to eliminate interference problems, embedded WiFi modules in devices should be designed to operate flexibly across the frequency range.
3. Information Security
Regardless of the type of connected device, if it is not designed correctly, it is bound to be accompanied by information security risks. The devices can be vulnerable to hacking, leading to data breaches and other security threats. It is essential to implement security protocols such as encryption and authentication to ensure the safety of devices.
Best Practices for Integrating Embedded WiFi Modules
1. Antenna Design
The antenna design within the module is crucial to achieving seamless connectivity. An antenna design should be based on factors such as range, interference, and power consumption. The size and placement of the antenna within the device should be considered the first priority in the overall design, as well as the antenna's frequency range. A well-designed antenna can improve the range and performance of the device, while a poorly designed antenna can lead to interference and reduced connectivity. Manufacturers should carefully select and test the antenna to ensure optimal performance.
Read More:How 5G Change the Game of Mechanical Design in Handheld Devices?
2. Power Consumption Management & Firmware Updates
When integrating embedded WiFi modules into devices, efficient power management can extend battery life and reduce power consumption, and the management of power consumption is also an important aspect of firmware management. Therefore, brand owners should provide regular firmware updates to continuously ensure information security and improve performance. Devices should also be designed to support over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates to simplify the update process even more.
3. Testing and Validation
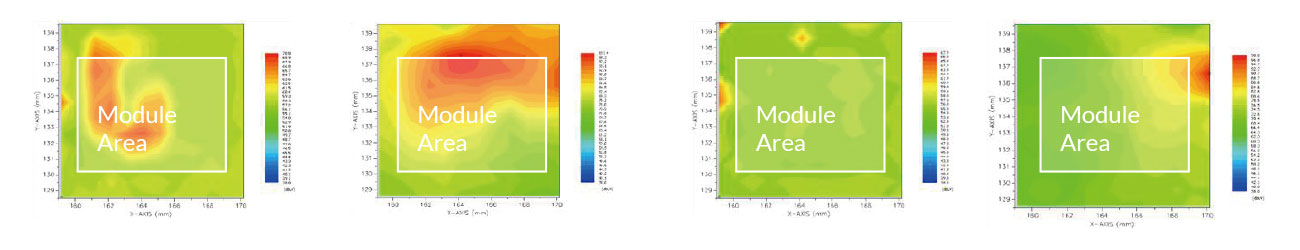
Brand owners should apply simulation in designing early-stage products to evaluate antennas' properties and performances, ensuring they meet the specifications to pass validation testing. The simulation data of authentic products can help spot potential problems before mass production. In this way, the design can be modified to prevent the functional problems that would appear after mass production, leading to product failure. At the same time, in addition, customized protocol development and validation can be ready according to the requirements of different telecommunication operators and regulations.
Read More:USI 5G Protocol Development & Validation: Last Mile for 5G Products
Expected Future of Embedded WiFi Modules
With advances in wireless technology and the growing demand for Internet of Things devices, consumers have come to expect and imagine more from Internet connectivity, with technologies such as WiFi 6, WiFi 7, 5G, edge computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning driving innovation in the field. With years of experience in WiFi module design, manufacturing, and validation, USI offers a full range of customized services to ensure that the modules can be integrated into our customers' products.
Combined with System in Package (SiP) technology, this will enable the design and manufacture of highly integrated, compact WiFi modules, which are particularly suitable for miniaturized products in pursuit of small dimensions. As a result, USI can produce smaller, higher-performance WiFi modules without sacrificing performance or reliability. As semiconductor technology begins to dominate the heart of global communications products, embedded WiFi modules are expected to be a key player in driving the next generation of smart devices.
Keep up with top trending topic
For the latest innovation technology, application
and industry insight.
Subscribe Our Blog
For the latest innovation technology, application
and industry insight.